We are honouring the FeDIOSci Award for the first time this year.
This funding supports innovative project ideas from young scientists at the interface of bone and the immune system at the Erlangen, Dresden, Ulm and Dortmund sites.
It is an opportunity for young scientists to receive financial support to work on an innovative project idea within osteoimmunology. In this way, preliminary data can be obtained that will ideally lead to an own project within the framework of the second funding period of DIONE.
We are looking for project approaches that ideally lead to an expansion of DIONE’s research activities in terms of content, that dare to think outside the box, have future potential and are translationally orientated. This year, one to two ideas will be supported with a one-off grant totalling 8,000 euros for material resources or support for personnel costs.
Applications are open to doctoral candidates and postdoctoral researchers who are employed at one of the universities or research institutions participating in DIONE, whose doctorate is expected to be completed in 2026 or whose doctorate was completed no more than 6 years ago at the time of the call for applications. In accordance with the DFG guidelines for early career researchers, parental leave of two years per child will be taken into account.
Take the opportunity and apply for your own mini-project.
Submit your project idea here
Application deadline: Mai, 15th 2025
If you need further information, please do not hesitate to contact the DIONE branch office
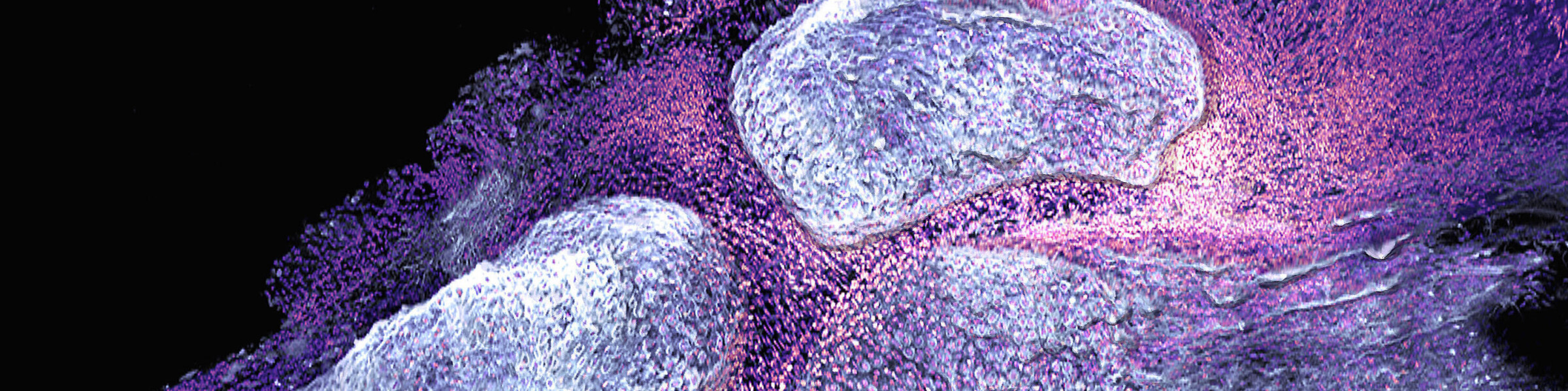
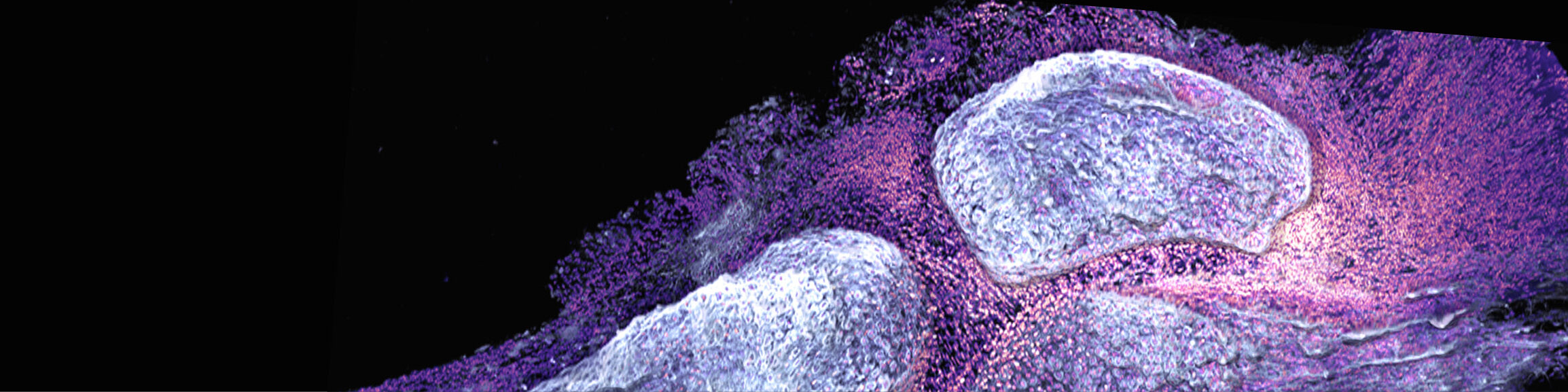
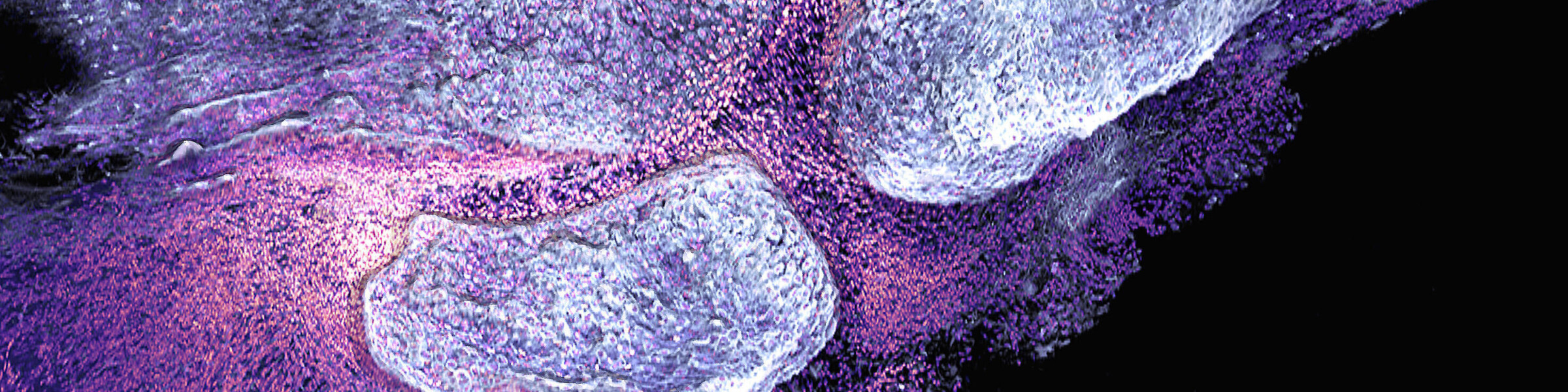
New paper published: L-arginine as a booster of bone health?
Could a common amino acid prove to be a potential therapeutic agent for the reduction of arthritis and bone loss?
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) affects millions of people worldwide, causing joint pain and bone loss due to the excessive activity of bone-resorbing cells, known as osteoclasts. The latest research findings indicate that L-arginine, a common amino acid, may play a pivotal role in the inhibition of this destructive process. It was discovered that L-arginine has the capacity to „reprogram“ osteoclasts, effecting a transition in their energy production from a process that is conducive to bone loss to one that is inhibitory. By modifying the cells‘ metabolism, L-arginine effectively reduces osteoclast formation and activity, resulting in reduced bone erosion. This discovery provides a potential avenue for developing new treatments for RA that utilise the properties of this amino acid to protect our bones. Could L-arginine supplements become a simple and effective strategy to combat arthritis and preserve bone health? Our findings suggest that this is a possibility that warrants further investigation.
Read more here ⬇
https://doi.org/10.1136/ard-2022-223626
Start of the 1st DIONE Trainingsweek
We’re thrilled to announce the kickoff of the #TRR369 #DIONE Student Training Week focused on #inflammation models! 🧬
Young scientists are coming together to deepen their knowledge and skills in cutting-edge osteoimmunology research. 🧑🔬👩🔬
With a focus on understanding the complex link between inflammation and #bone #health, this week is all about hands-on learning, human inflammatory diseases and collaboration across disciplines. 🌍🔬
Stay tuned for updates and breakthroughs from these rising stars in research! ✨💡